There is a wealth of Strategic Planning content
here, developed over the years from very successful
entrepreneurs, corporate executives, marketing
professionals and some incredibly talented sales
managers. In addition, Ryan Hixenbaugh spent years
in the Advertising Agency business prior to starting
Stratcom, a strategic planning and outsource
marketing service.
The Site includes some of the basics of Strategic
Planning, as well as advanced thinking that may
spark for your own planning. Ideas lead to
ideas.
The content is for sharing. It certainly isn't
ours alone, but comes from many other thinkers, most
of which we've tried to attribute. Use the
information or add to it and debate it with the
Facebook link to RyanHixenbaugh.
Bookmark the site or send the link to others on your
management team.
Feel free to link to the site using
www.RyanHixenbaugh.com
If you like the thinking or need additional help,
contact Ryan with comments, questions OR to add
talent to YOUR Team.
Each year companies undertake several major planning
exercises.
The Sales Team builds a Sales Forecast.
Based on that forecast, the Executive Team
establishes a Budget Plan.
The third major program is the Strategic Plan. This
plan assesses the markets and competitors, internal
resources and capabilities and external influences
to establish a strategic approach to growing the
business.An
MBA Program will illustrate the Strategic Planning
Process as:
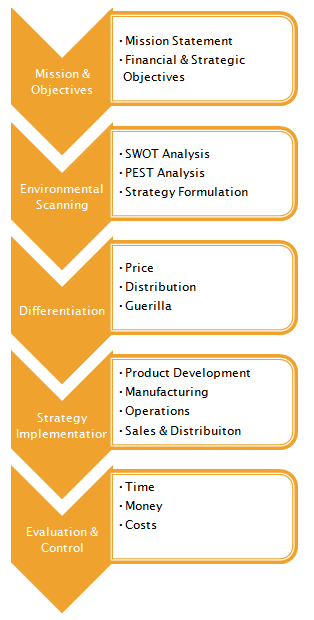
The mission statement
and setting objectives are commonplace activities.
Most folks are familiar with the SWOT and PEST
Analysis that make up the Environmental Scan.
A refresher is listed below.
Back to top
SWOT Analysis
Environmental Scan
This is a way of reviewing the company both
internally and the larger marketplace externally.
Strengths and Weaknesses are internal factors and
considers capital, credit, cash, R&D, manufacturing,
shipping, the sales
organization, marketing, human resources etc.
Opportunities and Threats focus on external factors
such as demand, competition, advancing technology
and trends. An analysis
summary may look like this with the boxes filled.
|
Attribute |
Strength |
Weakness |
|
Brand Equity |
|
|
|
Product Delivery |
|
|
|
Patents |
|
|
|
Manufacturing/Shipping |
|
|
|
Product
Lifecycle |
|
|
|
Proprietary Cost
Advantage |
|
|
|
Sales
Organization |
|
|
|
Distribution |
|
|
|
Attribute |
Opportunity |
Threat |
|
Demand
|
|
|
|
Technology |
|
|
|
Regulatory
Environment |
|
|
|
Substitutions |
|
|
|
Market Trends |
|
|
|
Weather |
|
|
Once you’ve identified and evaluated
the SWOT elements, you can prioritize the strategic
significant with a
TOWS Matrix.
|
|
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|
Opportunities |
Strength/Opportunities |
Weakness/Opportunity |
|
Threats |
Strength/Threat |
Weakness/Threat |
SWOT Strategic Analysis
| |
Strength/Opportunity Strategies |
|
High Potential
Opportunities |
| |
Weakness/Opportunity Strategies |
|
Plan to address
internal weakness |
| |
Strength/Threat
Strategies |
|
Apply strengths
to manage external vulnerability |
| |
Weakness/Threat
Strategies |
|
High
vulnerability and risk external threat
Establish defensive plan |
Back to top
PEST Analysis
(Political, Economic, Social, Technological)
A
second part of the Environmental Scan is the PEST
Analysis considering:
Political Factors
Political Stability
or Party Agendas
Environmental Regulations
Trade Restrictions & Tariffs
Labor Laws & Minimum Wage
Tax Policies
Political factors
today will be affecting:
-
The oil industry
as the BP spill resolves
-
Changes in
access and reimbursement to healthcare
-
Changing
regulations in Securities and Banking
-
Changing laws on
marijuana use.
Economic Factors
Economic Growth
Interest Rates
Exchange Rates
Inflation Rates
Economic factors are
a consideration today for:
-
Credit with the
current budget deficits
-
Current
unemployment levels
-
The changing
fortunes of Baby Boomers entering retirement
-
The tax
consequence of budget deficits
Social Factors
Baby Boom Affect
Generational Attributes
Health Trends
Health Consciousness
Social Factors for
consideration are:
Technological Factors
Rate of
Technological Change
The reduced price affect of technology
The increased rate of adoption for technology
R&D Activity
Government technology incentives
Technological
Factors active in the marketplace include:
-
The shifting
market positions of Microsoft, Google &
Apple
-
The shift
towards cloud computing
-
Electric
vehicles & alternative fuels
-
The integration
of computerization & everything
Back to top
 Sales
Planning Sales
Planning
Strategic Touch Points
Stratcom developed
the following elements for a National Sales
Strategic Plan. (Regional Plans and
Rollouts have a different though similar
emphasis).
Some companies have
the reporting for this analysis and have already
made use of it in their daily operations.
Others have not. Focus on what you
haven’t accessed.
That's where the discussion and work will lead
to real gains.
As a step by step
process to establishing a strategic plan,
Stratcom follows this critical path method to
quickly ramp up and pinpoint critical areas and
strategic opportunities. These items will
help facilitate your SWOT and PEST Analysis.
These are the key
touch points in Strategic Planning.
Statistical Sales Performance Review
LY Sales Nationally
Current Year Growth Objective
Percentage Sales to Plan
Number of Accounts
National Average Annual Sales Figure
National Mean Annual Sales Figure
Run the same statistics by territory
Marketplace Review
Market Size by
Distribution Channel
Competitive Market Shares
Product Status
Is this a
differentiated or commodity product?
Is there established demand?
It this an emerging industry (primary demand) or
a mature industry (secondary demand)
Who is the market leader and what is their
estimated market share?
Sales Coverage Evaluation
#1 Coverage of
the Top 50 Metropolitan Statistical Areas
#2 Average active accounts per territory
#3 Market penetration comparison
Identify potential customers in the market
though a standardized source
(trade association, SIC number or such)
Divide the number of customers by dollar sales.
Result is the Dollars per Customer.
Use this figure to compare market penetration
between territories.
Distribution channels.
What is the call
pattern for the product?
Who makes the decision?
Who makes the purchase?
What other channels might be involved?
Who can influence the sale?
Sales Cycle
What is the selling
cycle for key products?
Is this a major purchase for the average
prospect?
What is the buying process for an average
customer?
How long does it take a prospect to complete the
process and make a purchase?
Commissions
What should a sales
person earn?
Will that level of income earn sufficient
attention from the sales professional?
What must they sell to earn that income?
What is the average/mean sales earning
currently?
Is this a Mortgage Line or a Vacation Line?
The lines that pay
for a sales professional’s mortgage get primary
attention. Smaller line may make a car payment
or pay for an annual vacation. In the
salesperson’s world, these lines are going to
get less attention. Is your product line a
mortgage line or a vacation line You need
to be realistic on this to set accurate sales
expectations.
Competition
How many sales
associates does the market leader have?
Is this typical for the niche?
Summary
This information is not the
Strategic Plan. It guides that
plan. It suggests topics to discuss and
resolve before setting the objectives and
building that plan. Identifying weakness
does not mean accepting them and building around
them. It means exploring and addressing
them before the plan.
Until the above elements and been
collected, reviewed and discussed, you are not
ready for the creative portion of the plan.
Back to
top
Product Launches
The Role of New Products
New products are
important because they generate sales.
Not because they are ‘new,’ but because of the
dynamics that surround them.
There are five things that happen with a product
launch that make them successful.
In order to maximize the effect of a new
product, Marketing and Product Development must
manage the launch to achieve the benefit of
these five elements.
#1. New
products make a company vital and relevant in
the marketplace
It helps the company attract attention.
#2. New
products give a reason for a sales associate to
make calls.
It is a new story and a new reason to talk to
key accounts and prospects.
They revitalize the sales force.
#3. New
products give the customer a reason to spend
time with the sales force.
Customers need and want to stay on top of market
developments.
They want to learn about new product
opportunities.
#4. New
products force prospects to evaluate:
-
Their current
product offering. Is it better, worse
or same as what they are currently using;
-
Their current
manufacturer. Are they regularly doing
new and interesting things? Are they
leading the industry?
-
Their current
rep. Does the current rep bring new
opportunities by?
-
Have they seen
their current rep recently? How do
they compare with this new guy?
#5. New
products provide a sales spike.
If only due to trial from key accounts and rep
relationships. Some sales spikes sustain,
others don’t. But new launches
generate short term sales results due to the
above four points.
Effective Product Launches
New products should
be planned based on maximizing these five
factors.
It takes considerable time, money and creative
talent to develop a new product.
Product Managers deserve a sales force that
maximizes these efforts.
Take each new product very seriously and provide
it sufficient support to be effective.
Rule #1:
Product launches are money. Do not delay
them. When they are ready – go!
Therefore it is the responsibility of Product
Development to schedule development to coincide
with market opportunities. Missing market
opportunities with launch delays will reduce the
success of a launch.
Plan the calendar and hit the deadlines.
Launch Planning
1) Pre-Launch
Testing
Testing is necessary for the Product Manager to
evaluate performance.
But there is also a sales effect. When
possible, test products through key accounts.
Engage your customers. Let them feel
involved and respected. Give them
ownership of the product.
Their initial orders (based on their
participation) are the foundation to a launch.
2) Pre-Launch
Evaluation
Take prototypes to Trade Shows to ‘share’ with
key accounts. Don’t sell them.
Talk about them. Ask opinions. Share
discreetly. Let the key accounts feel the
importance of their opinions.
3) Trade Show
Introduction
Time product launches for major trade shows.
Hitting these deadlines is the responsibility of
Product Management. Launches are
significantly weakened when you miss a major
gathering with the chance to create industry
buzz. What are your two most important
conferences of the year? Every year, plan
to introduce something new at them.
4) Field
Launch
The field launch must be coordinated and
complete.
That means the reps receive everything they need
to successfully place the product.
They receive it completed and together,
including:
-
Samples
-
Product Profile
What is the product and what does it do?
-
Training (live,
webinar, printed, binder, teleconference)
-
How is it
different than the competition?
Provide a competitive matrix showing product
comparisons, including price.
-
Technical
training. How does it work? How
to you apply it?
-
What is the
sales strategy? What do people buy?
-
Sales support
materials
Specifications
Sales literature
Ordering forms
-
Marketing
Inbound Marketing launch
Social Networks Launch
Product Announcements
Trade Show impact
Price sheets
Web Site Introductory campaign
-
Customer Service
training
Full, hands-on awareness of the product
-
Sales Rep
Expectations
Dollars & Units for first 90 days
(preferably by Key Account)
Key Account time frame
Perhaps a contest, promotion or incentive
Offer recognition for performance
Induce competitive spirit
Measure and report
5) 90 Day Time
Frame
Focus on the launch
long enough for it to succeed.
In that time frame the expectation is that every
sales person will simultaneously be in the
market promoting the new product.
-
This kind of
national activity generates ‘buzz.’
-
It assures that
every rep is learning to sell the product.
They need to present it a few times to learn
how to sell it. If they don't do that
now, it may never become part of their
repertoire.
It takes time to
digest the materials, build confidence, schedule
and visit all key accounts and prospects.
During that time frame, don’t distract the sales
force with other launches, promotions or
requirements. Focus on seating the product
in the product arsenal. Otherwise, you
aren't getting the full bang for your R&D
dollar.
If new products take
about 90 days to generate their effect, it
stands to reason that four major product
launches a year are about all the sales
organization can emphasize.
Back to top
 Sales
Literature Sales
Literature
There are all kinds of sales literature that play
different roles for the sales professional. It
is important that you understand what Sales needs to
be successful and deliver them the appropriate tool.
Here are some considerations.
Catalogs
This is a primary sales tool and is often
misused.
Catalogs bring the entire line together, so
management loves them.
Often four color and multiple pages, they are
expensive to create.
They can also go out of date fairly quickly (as
soon as a new product is introduced).
Key Message:
The key message of a catalog is the breadth of
the line.
It shows buyers everything they can get from the
manufacturer. Catalogs help customers
reference other 'commodity' products offered by
the company that don't receive sales focus.
Vulnerability:
Because it includes so many products, the
information is typically short and
specification driven. Product sell is
usually minimal. Due to the size, it is awkward
for the sales person to reference and use. It is
expensive to give away (particularly to
unqualified leads).
User: Catalogs
are a good tool for customers to reference
product number, specifications and order
procedures. Typically the catalog is filed
away for reference by someone placing an order
with the company. It is not used by the
decision makers.
Summary: Catalogs are for a
buyer's ordering convenience. They are not
for Sales to opening accounts. Before you
invest all that money on 24 pages of 4 color,
make sure you have the tools Sales needs to
generate new business.
Sales Sheets
Sales sheets are a single page, front and
back. They focus on the key selling proposition
of the product. They are a very powerful
tool in the hands of the rep to add visuals,
bullet points and credibility to the
presentation. Sales sheets are single minded,
focused on a single product and selling it. They
are inexpensive to handout.
A secondary benefit
of the sales sheet is for training the sales
force. If a rep hasn’t emphasized a
particular product for awhile, the sales sheet
reminds them exactly how to sell it. The sales
sheet is the selling
strategy.
Brochures
Multiple page (four or eight page) brochures
give extra strength and credibility to a lead
product or a product category. They offer
more production value than a sales sheet, so are
saved for more profitable segments of the line.
They require the additional space to present
multiple products within the segment.
Otherwise, brochures
work much like a sales sheet.
Back to top
How Stratcom Can
Help
The
problem with the MBA approach is that it is too
academic for the speed that most companies move.
In the exercise, they’ll spend quite a bit of time
on the analysis and attempting to articulate
something the entire executive team knows
intuitively. Once they finally articulate it, they
have the statement, but haven’t made any real
progress towards growing the company.
As
a Strategic Outsource, Stratcom will lead the
analysis, spending time focused on the
opportunities.
The critical path will look at:
Internal Review and Analysis
(SWOT)
Statistical Sales
Performance Review
Product Status
Sales Coverage Evaluation
Sales Cycle
Commissions
External Review and Analysis
(PEST)
Marketplace Review
Distribution channels.
Key Account Review
Competition
Strategic Plan
Elements
Sales Training
Regional Sales Management Guides
Effective Product Launches and Launch Planning
Sales Literature
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Social Network Strategies
The end result will be a well grounded annual
plan based on sales objectives and growth
targets a quarterly implementation guide.
Stratcom is available to manage the plan on a
monthly basis.
Back to top |